For many, solving a Rubik’s Cube is a difficult task that requires a lot of time and patience, but what if we could create a machine that could do it for us? That’s exactly what this project is all about - building an automatic Rubik’s Cube solver that can solve the puzzle in a matter of minutes using computer vision and advanced robotics technology.
The project started with researching various methods to solve the Rubik's Cube, starting with the ‘beginner's method’ and eventually settling on the ‘advanced CFOP’ method.
The Advanced CFOP method consists of four main steps:
- Cross: The first step is to solve the cross on the bottom face of the cube. This is done by placing four edge pieces in their correct positions and orientations.
- F2L: The second step is to solve the first two layers of the cube simultaneously using a set of algorithms. This involves pairing a corner and an edge piece and inserting them into their correct position in the top layer.
- OLL: The third step is to orient the last layer using a set of algorithms that involve rotating the cube to different positions.
- PLL: The final step is to permute the last layer (PLL) using a set of algorithms that involve swapping the positions of the last layer pieces.
The face color detection algorithm involving edge detection and color segmentation has been developed to accurately identify the colors of each face of the Rubik's Cube. An algorithm based on the above stated Advanced CFOP method was then used to generate a solution to the puzzle based on the current state of the cube, which was then tested in a simulation
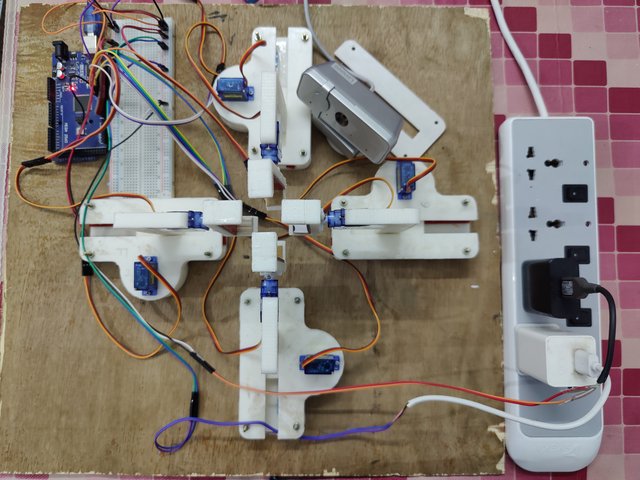
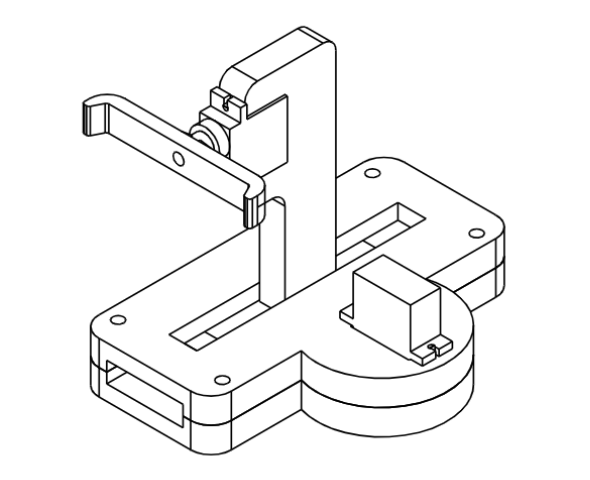
The CAD model for the project was designed and 3D printed. Each arm had to be precisely grated and evened to ensure proper balance and elevation. Friction was adjusted using tapes to ensure proper grip, resulting in a long-drawn process to ensure synchronized movement of each and every component. All components were then assembled to create the Rubik's Cube solving mechanism.
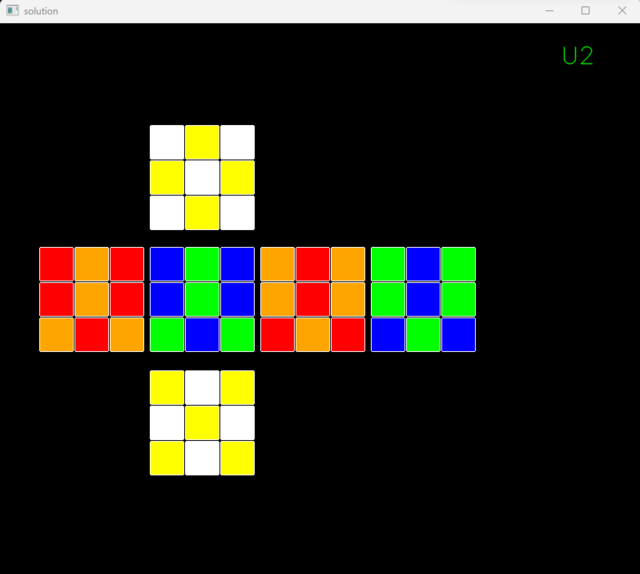
Functions have been developed for the 18 basic movements of the Cube (U, U’ ,U2, F, F’, F2, R, R’, R2, L, L’, L2, D, D’, D2, B, B’, B2) Various time delays were calculated and adjusted for each move to ensure synchronization between the simulation and hardware. The simulation and hardware were made to run in synchronism, allowing the solver to correctly execute the moves necessary to solve the Rubik's Cube.
- CAD Model - The mechanical components of the project are designed using CAD modeling software Solid Works to get the precise dimensions of each component.
- 3D Printing - The components designed are 3D printed using UltiMaker Cura. The 3D printed components are then assembled to create the mechanical structure of the Rubik's Cube solver.
- Motors - The solver uses a total of eight SG90 servo motors for its functioning. Servo motors provide very accurate rotation angle control as they use feedback control. These servo motors are small, cheap and provide a decent amount of torque, making them ideal for this project.
- Robotic arms - The mechanical structure of the Rubik's Cube solver consists of four arms for the four faces, with each arm containing one servo motor for rotating the face and one for linear motion.
- Webcam - The project uses a webcam to capture images of the Rubik's Cube's sides. These images are then processed to determine the color of each square on the Rubik's Cube.
- Arduino - The Rubik's Cube solver is controlled by an Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller board. This board is used because it is cost-effective, has a large number of ports and provides fast processing, which is required for the real-time processing of the images and the movement of the servo motors. The connections between the components are made using a breadboard, which is a temporary prototype board for connecting electronic components
- Power Source - The solver uses two 5V/2A power sources fed through mobile chargers connected in parallel to provide enough power to the motors
- Python - used for image processing, color detection, keyboard control and generating solution steps for the Rubik’s Cube
- C++ - used for writing code for the Arduino Board
- VSCode - used for developing and debugging the Python code
- Arduino IDE - used for writing, compiling and uploading the C++ code to the Arduino board
- cv2 - OpenCV computer vision library used for video capturing, image processing and displaying the simulation
- coloroma - uses the hsv (hue, saturation, value) parameters of the color space to detect the colors of the Rubik's Cube squares
- keyboard - used for automating the keystrokes for controlling the file upload to Arduino and switching the tabs
- kociemba - used for generating the solution steps for solving the Rubik’s Cube
- Initiating a file write to the Arduino board that contains the steps to show each face of the Rubik’s Cube to the webcam
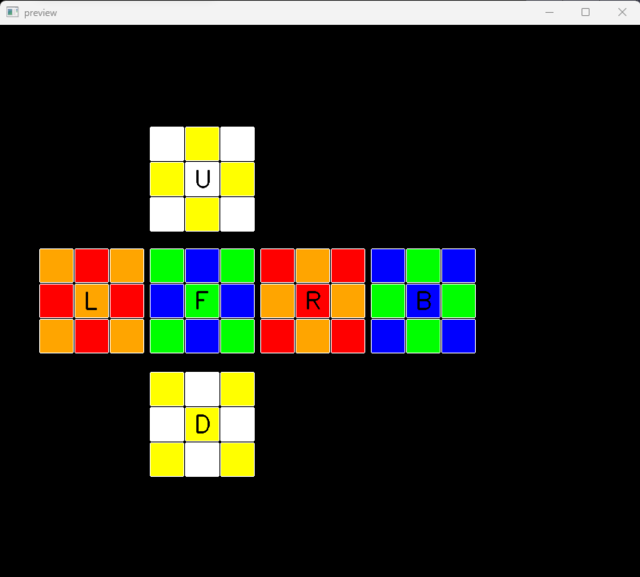
- Detecting the colors of each square of the Rubik’s Cube and mapping them to their respective faces
- Generating the solution steps to solve the Rubik’s Cube
- Initiating a second file write to the Arduino board that contains the steps to solve the Rubik’s Cube based on the generated solution
- Simulating the solution process of the Rubik’s Cube in real-time, which can be viewed simultaneously
- After the Rubik’s Cube is solved, destroying the file containing the solution to reset the whole process to the initial stage
-
Place the unsolved cube in the correct position - white center up and green center at front.
-
Ensure proper connections among the components and power supply to the servos.
-
Open the src folder both in VSCode and Arduino IDE, ensure no other windows are open.
-
Install the required python libraries by running the following commands in the terminal:
pip install cvzonepip install coloromapip install keyboardpip install kociemba -
Run the python file
main.pyto initiate the solving process. -
Ensure that you don’t disturb any of the windows while the Cube is getting solved.
The Rubik's Cube solver project has a lot of scope for improvement, and the following advancements can be made to achieve better speed, accuracy, and precision:
- Improvement in Color detection model can be made to increase the accuracy of color recognition. This could be achieved by using machine learning algorithms to train the model on a larger dataset of Rubik's Cube images and by fine-tuning the color recognition parameters allowing the system to learn and adapt to different lighting conditions, cube configurations, and color variations.
- Better algorithms can be developed to reduce the number of steps required to solve the Rubik's Cube.
- Using stepper motors instead of servos and changing the design to use 5/6 motors controlling the 5/6 faces rotations instead of eight motors could result in a more efficient design. This is because no linear motion is required since no flips are required, and thus fewer motors would be needed for the same functionality. This would reduce the overall cost and complexity of the project.
- Dynamic grasping techniques could be used to allow the mechanical arms to adapt their grip on the cube based on its position and orientation, improving the precision and reliability of the cube manipulation process.